Cloudera Hadoop Administrator Certification Certification Questions and Answer (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question
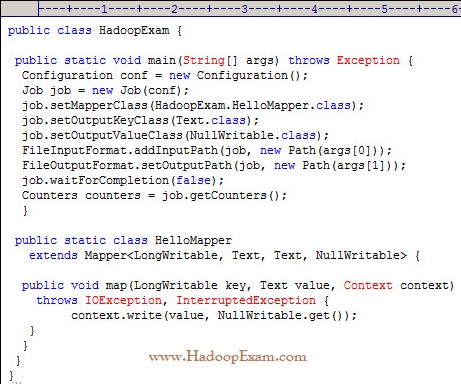
What happens when you run the below job twice , having each input directory as one of the data file called data.csv.
with following command. Assuming there were no output directory exist
hadoop job HadoopExam.jar HadoopExam inputdata_1 output
hadoop job HadoopExam.jar HadoopExam inputdata_2 output
1. Both the job will write the output to output directoy and output will be appended
2. Both the job will fail, saying output directory does not exist.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Both the job will successfully completes and second job will overwrite the output of first.
Ans : 3
Exp : First job will successfully run and second one will fail, because, if (output directory already exist then it will not run
and throws exception, complaining output directory already exist.
Question : You have a an EVENT table with following schema in the Oracle database.
PAGEID NUMBER
USER VARCHAR2
EVENTTIME DATE
PLACE VARCHAR2
Which of the following command creates the correct HIVE table named EVENT

1.
2.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4.
Ans : 2
Exp : The above is correct because it correctly uses the Sqoop operation to create a Hive table that matches the database table.
Option 3rd is not correct because --hive-table option for Sqoop requires a parameter that names the target table in the database.
Question : Please find out the three correct functionalities of the ResourceManager in YARN or MRv Hadoop Cluster.
1. Monitoring the status of the ApplicationMaster container and restarting on failure
2. Negotiating cluster resource containers from the Scheduler, tracking containter status, and monitoring job progress
3. Monitoring and reporting container status for map and reduce tasks
4. Tracking heartbeats from the NodeManagers
5. Running a scheduler to determine how resources are allocated
6. Archiving the job history information and meta-data

1. 2,3,5
2. 3,4,5
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 1,4,5
5. 1,2,6
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: The ResourceManager has two main components: Scheduler and ApplicationsManager.
The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to familiar constraints of capacities, queues etc.
The ResourceManger tracks heartbeats from the NodeManagers to determine available resources then schedules those resources based on the scheduler specific configuration.
The ApplicationsManager is responsible for accepting job-submissions, negotiating the first container for executing the application specific ApplicationMaster and provides the service for restarting the ApplicationMaster container on failure.
The per-application ApplicationMaster has the responsibility of negotiating appropriate resource containers from the Scheduler, tracking their status and monitoring for progress. Depending on the type of application, this may include monitoring the map and reduce tasks progress, restarting tasks, and archiving job history and meta-data.
The NodeManager is the per-machine framework agent who is responsible for containers, monitoring their resource usage (cpu, memory, disk, network) and reporting the same to the ResourceManager/Scheduler.
Question : In MRv YARN Hadoop Infrastructure where does MapReduce intermediate data as an output of Mappers will be stored.

1. In HDFS, in the job's output directory
2. In HDFS, in a temporary directory defined by mapred.tmp.dir
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. On the underlying filesystem of the ResourceManager node
5. On the underlying filesystem of the local disk of the node on which the Reducer will run, as specified by the ResourceManager
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer : The local directory where MapReduce stores intermediate data files is specified bymapreduce.cluster.local.dir property. You can specify a comma-separated list of directories on different disks on the node in order to spread disk i/o. Directories that do not exist are ignored.
Question : As part of QuickTechie Inc Hadoop Administrator you have upgraded your Hadoop cluster from MRv to MRv, Now you have
to report your manager that, how would you determine the number of Mappers required for a MapReduce job in a new cluster.
Select the correct one form below.

1. The number of Mappers is equal to the number of InputSplits calculated by the client submitting the job
2. The ApplicationMaster chooses the number based on the number of available nodes
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. NodeManager where the job's HDFS blocks reside
5. The developer specifies the number in the job configuration
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Each Mapper task processes a single InputSplit. The client calculates the InputSplits before submitting the job to the cluster. The developer may specify how the input split is calculated, with a single HDFS block being the most common split. This is true for both MapReduce v1 (MRv1) and YARN MapReduce implementations.
With YARN, each mapper will be run in a container which consists of a specific amount of CPU and memory resources. The ApplicationMaster requests a container for each mapper. The ResourceManager schedules the resources and instructs the ApplicationMaster of available NodeManagers where the container may be launched.
With MRv1, each Tasktracker (slave node) is configured to handle a maximum number of concurrent map tasks. The JobTracker (master node) assigns a Tasktracker a specific Inputslit to process as a single map task.
Related Questions
Question :
What is PIG?

1. Pig is a subset fo the Hadoop API for data processing
2. Pig is a part of the Apache Hadoop project that provides scripting languge interface for data processing
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. None of Above
Question : What is distributed cache?

1. The distributed cache is special component on namenode that will cache frequently used data for faster client response.
It is used during reduce step
2. The distributed cache is special component on datanode that will cache frequently used data
for faster client response. It is used during map step
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. The distributed cache is a component that allows developers to deploy jars for Map-Reduce processing.
Question : You already have a cluster on the Hadoop MapReduce MRv, but now you have to upgrade the same on MRv but somehow
your management is not agreeing to install Pig. And you have to convince your management for installing the Apache Pig in Hadoop Cluster.
Which is the correct statement which you can use to show the relationship between MapReduce and Apache Pig?

1. Apache Pig rely on MapReduce which allows to do special-purpose processing not provided by MapReduce.
2. Apache Pig comes with no additional capabilities to MapReduce. Pig programs are executed as MapReduce jobs via the Pig interpreter.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Apache Pig comes with the additional capability of allowing you to control the flow of multiple MapReduce jobs.
Question : Prior to Hadoop .., the NameNode was a single point of failure (SPOF) in an HDFS cluster. Each cluster had a single NameNode,
and if that machine or process became unavailable, the cluster as a whole would be unavailable until the NameNode was either restarted
or brought up on a separate machine.Select all the actions you can accomplish once you implement HDFS High Availability on your Hadoop cluster.
1. Automatically replicate data between Active and Passive hadoop clusters.
2. Manually 'fail over' between Active and passive NameNodes
3. Automatically 'fail over' between Active and Passive NameNodes if Active one goes down.
4. Shut Active NameNode down for maintenance without disturbing the cluster.
5. Increase the parallelism in existing cluster.

1. 1,3,4
2. 2,3,4
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. All 1,2,3,4,5
Question : You have a website www.QuickTechie.com, where you have one month user profile updates log. Now for the classification analysis
you want to save all the data in a single file called QT31012015.log which is approximately in 30GB in size. Now you are able to push
this full file in a directory on HDFS called /log/QT/QT31012015.log, select the correct statement for the pushing the file on HDFS.

1. The client queries the NameNode, which returns information on which DataNodes to use and the client writes to those DataNodes
2. The client writes immediately to DataNodes based on the cluster's rack locality settings
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. The client writes immediately to DataNodes at random
Question : Select the appropriate way by which NameNode get to know all the available DataNodes in the Hadoop Cluster.

1. DataNodes are listed in the dfs.hosts file. The NameNode uses that as the definitive list of available DataNodes.
2. DataNodes heartbeat in to the master on a time-interval basis.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. The NameNode broadcasts a heartbeat on the network on a regular basis, and DataNodes respond.