Oracle Java Programming Certification Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : Which three statements are true about the structure of a Java class?
A. A class can have only one private constructor.
B. A method can have the same name as a field.
C. A class can have overloaded static methods.
D. A public class must have a main method.
E. The methods are mandatory components of a class.
F. The fields need not be initialized before use.

1. A,B,C
2. B,C,D
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. D,E,F
5. A,E,F
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation:
A: Private constructors prevent a class from being explicitly instantiated by its callers. If the programmer does not provide a constructor for a class, then the system will always
provide a default, public no-argument constructor. To disable this default constructor, simply add a private no-argument constructor to the class. This private constructor may be empty.
B: The following works fine:
int counter() {
int counter=0;
return (1);
}
C: We can overload static method in Java. In terms of method overloading static method are just like normal methods and in order to overload static method you need to provide another
static method with same name but different method signature.
Incorrect:
Not D: Only a public class in an application need to have a main method.
Not E: Example:
class A
{
public string something;
public int a;
}
Q: What do you call classes without methods? Most of the time: An anti pattern. Why?
Because it faciliates procedural programming with "Operator" classes and data structures. You separate data and behaviour which isn't exactly good OOP.
Often times: A DTO (Data Transfer Object)
Read only datastructures meant to exchange data, derived from a business/domain object.
Well sometimes, you just gotta have those structures to hold data that is just plain and simple and has no operations on it.
Not F: Fields need to be initialtized. If not the code will not compile. Example: Uncompilable source code - variable counter might not have been initialized
Question : Which two items can legally be contained within a java class declaration?
A. An import statement
B. A field declaration
C. A package declaration
D. A method declaration

1. A,B
2. B,C
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. B,D
5. A,D
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Question : Which two may precede the word 'class' in a class declaration?
A. local
B. public
C. static
D. volatile
E. synchronized

1. A,B
2. B,C
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. D,E
5. A,E
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation:
B: A class can be declared as public or private.
C: You can declare two kinds of classes: top-level classes and inner classes. You define an inner class within a top-level class. Depending on how it is defined, an inner
class can be one of the following four types: Anonymous, Local, Member and Nested toplevel.
A nested top-level class is a member classes with a static modifier. A nested top-level class is just like any other top-level class except that it is declared within another class
or interface.
Nested top-level classes are typically used as a convenient way to group related classes without creating a new package. The following is an example: public class Main
{
static class Killer
{
Related Questions
Question : Given the following two classes:
How should you write methods in the ElectricAccount
class at line n1 so that the member variable
bill is always equal to the value of the member
variable kwh multiplied by the member variable rate?
Any amount of electricity used by a customer
(represented by an instance of the customer class)
must contribute to the customer's bill
(represented by the member variable bill)
through the method useElectricity method.
An instance of the customer class should never be able to tamper
with or decrease the value of the member variable bill.

1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Question :

1. A,B
2. B,C
3. A,C
4. D,E
4. A,E
Question : Given:
Car c1 = new Car("Auto");
Car c2 = new Car("4W" , 150 , "Manual");
System.out.println(c1.type + " " + c1.maxSpeed + " " + c1.trans);
System.out.println(c2.type + " " + c2.maxSpeed + " " + c2.trans);
What is the result?

1. 4W 100 Auto
4W 150 Manual
2. Null 0 Auto
4W 150 Manual
3. Compilation fails only at line n1
4. Compilation fails only at line n2
5. Compilation fails at both line n1 and line n2
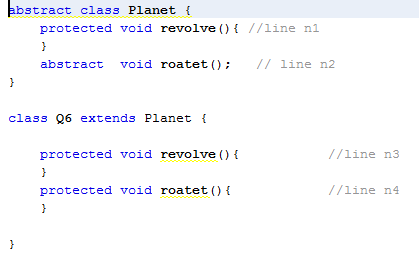
Question : Which two modifications,
made independently, enable the code to compile?
A. Make the method at line n1 public.
B. Make the method at line n2 public.
C. Make the method at line n3 public.
D. Make the method at line n3 protected.
E. Make the method at line n4 public.
1. A,B
2. B,C
3. C,D
4. D,E
Question : What is the name of the Java concept that uses access modifiers to protect variables and hide
them within a class?

1. Encapsulation
2. Inheritance
3. Abstraction
4. Instantiation
5. Polymorphism
Question : Given the code fragment:
public static void main(String[] args){
short s1 = 200;
Integer s2 = 400;
Long s3 = (long) s1+s2; //line n1
String s4 = (String)(s3*s2); //line n2
System.out.println("Sum is " + s4);
}
What is the result?

1. Sum is 600
2. Compilation fails at line n1.
3. Compilation fails at line n2.
4. A ClassCastException is thrown at line n1.
5. A ClassCastException is thrown at line n2.