Cloudera Hadoop Administrator Certification Certification Questions and Answer (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : You have a website www.QuickTechie.com, where you have one month user profile updates log. Now for the classification analysis
you want to save all the data in a single file called QT31012015.log which is approximately in 30GB in size.
Now you are able to push this full file in a directory on HDFS called /log/QT/QT31012015.log. Now you also get to know
you can store the same data in the HBase as well, because it provides ...

1. Random writes
2. Fault tolerance
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Batch processing
5. 2,3
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: When Would I Use Apache HBase?
Use Apache HBase when you need random, realtime read/write access to your Big Data. This project's goal is the hosting of very large tables -- billions of rows X millions of columns atop clusters of commodity hardware. Apache HBase is an open-source, distributed, versioned, non-relational database modeled after Google's Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data by Chang et al. Just as Bigtable leverages the distributed data storage provided by the Google File System, Apache HBase provides Bigtable-like capabilities on top of Hadoop and HDFS.Apache HBase provides random, realtime read/write access to your data. HDFS does not allow random writes. HDFS is built for scalability, fault tolerance, and batch processing.
Features
Linear and modular scalability.
Strictly consistent reads and writes.
Automatic and configurable sharding of tables
Automatic failover support between RegionServers.
Convenient base classes for backing Hadoop MapReduce jobs with Apache HBase tables.
Easy to use Java API for client access.
Block cache and Bloom Filters for real-time queries.
Query predicate push down via server side Filters
Thrift gateway and a REST-ful Web service that supports XML, Protobuf, and binary data encoding options
Extensible jruby-based (JIRB) shell
Support for exporting metrics via the Hadoop metrics subsystem to files or Ganglia; or via JMX
Question : You have setup a Hadoop Cluster in Norman data center, and having all the settings as default., how much data will you be able to store on
your Hadoop cluster if it has 12 nodes with 4TB of raw disk space per node allocated to HDFS storage?

1. Nearly 3TB
2. Nearly 12TB
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Nearly 48TB
5. Can not calculate
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: These instructions for cluster configuration assume that you have already downloaded and unzipped a copy of Hadoop. Module 3 discusses getting started with Hadoop for this tutorial. Module 7 discusses how to set up a larger cluster and provides preliminary setup instructions for Hadoop, including downloading prerequisite software.
The HDFS configuration is located in a set of XML files in the Hadoop configuration directory; conf/ under the main Hadoop install directory (where you unzipped Hadoop to). The conf/hadoop-defaults.xml file contains default values for every parameter in Hadoop. This file is considered read-only. You override this configuration by setting new values in conf/hadoop-site.xml. This file should be replicated consistently across all machines in the cluster. (It is also possible, though not advisable, to host it on NFS.)In cluster we have 12 nodes, each with 4TB of disk space allocated to HDFS, you have a total of 48TB of space available. 48/3 = 16, so you can store approximately 16TB of data.
Configuration settings are a set of key-value pairs of the format:
property-name
property-value
Adding the line final -- true inside the property body will prevent properties from being overridden by user applications. This is useful for most system-wide configuration options.By default, Hadoop replicates each HDFS block three times.
Question : You have a website www.QuickTechie.com, where you have the entire user profiles stored in the MySQL database.
Now you want to fetch everyday new profiles from this database and store into the HDFS as log file, also you wanted
to have POJO's created to interact with the imported data. Select the tool which perfectly solves above problem.

1. Oozie
2. Hue
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Sqoop
5. Pig or Hive
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer : Apache Sqoop(TM) is a tool designed for efficiently transferring bulk data between Apache Hadoop and structured datastores such as relational databases.Sqoop ("SQL-to-Hadoop") is a straightforward command-line tool with the following capabilities: Imports individual tables or entire databases to files in HDFS , Generates Java classes to allow you to interact with your imported data, Provides the ability to import from SQL databases straight into your Hive data warehouse. After setting up an import job in Sqoop, you can get started working with SQL database-backed data from your Hadoop MapReduce cluster in minutes.
The input to the import process is a database table. Sqoop will read the table row-by-row into HDFS. The output of this import process is a set of files containing a copy of the imported table. The import process is performed in parallel. For this reason, the output will be in multiple files. These files may be delimited text files (for example, with commas or tabs separating each field), or binary Avro or SequenceFiles containing serialized record data.
A by-product of the import process is a generated Java class which can encapsulate one row of the imported table. This class is used during the import process by Sqoop itself. The Java source code for this class is also provided to you, for use in subsequent MapReduce processing of the data. This class can serialize and deserialize data to and from the SequenceFile format. It can also parse the delimited-text form of a record. These abilities allow you to quickly develop MapReduce applications that use the HDFS-stored records in your processing pipeline. You are also free to parse the delimiteds record data yourself, using any other tools you prefer. Please refer Hadoop Professional Recorded Training provided by HadoopExam.com
Related Questions
Question : You have GB of memory available in your cluster. The cluster's memory is shared between
three different queues: public, manager and analyst. The following configuration file is also in place:
A job submitted to the public queue requires 10 GB, a job submitted to the maanger queue requires 30 GB,
and a job submitted to the analyst queue requires 25 GB. Given the above configuration,
how will the Fair Scheduler allocate resources for each queue?
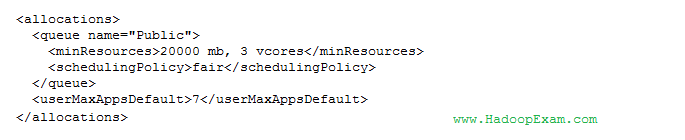
1. 40 GB for Public queue, 0 GB for Manager queue and 0 GB for Analyst queue
2. 10 GB for Public queue, 30 GB for Manager queue and 0 GB for Analyst queue
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 20 GB for the Public queue, 10 GB for the Manager queue, and 10 GB for the Analyst queue
Question : You have configured the Fair Scheduler on your Hadoop cluster. You submit a Equity job so that ONLY job Equity is
running on the cluster. Equity Job requires more task resources than are available simultaneously on the cluster. Later you submit ETF job.
Now Equity and ETF are running on the cluster at the same time.
Identify aspects of how the Fair Scheduler will arbitrate cluster resources for these two jobs?
1. When job ETF gets submitted, it will be allocated task resources, while job Equity continues to run with fewer task resources available to it.
2. When job Equity gets submitted, it consumes all the task resources available on the cluster.
3. When job ETF gets submitted, job Equity has to finish first, before job ETF can be scheduled.
4. When job Equity gets submitted, it is not allowed to consume all the task resources on the cluster in case another job is submitted later.

1. 1,2,3
2. 2,3
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 1,2,4
5. 1,2
Question : In the QuickTechie Inc. you have upgraded your Hadoop Cluster to MRv and in which you are
going to user FairScheduler. Using this scheduler you will which of the following benefit.
1. Run jobs at periodic times of the day.
2. Ensure data locality by ordering map tasks so that they run on data local map slots
3. Reduce job latencies in an environment with multiple jobs of different sizes.
4. Allow multiple users to share clusters in a predictable, policy-guided manner.
5. Reduce the total amount of computation necessary to complete a job.
6. Support the implementation of service-level agreements for multiple cluster users.
7. Allow short jobs to complete even when large, long jobs (consuming a lot of resources) are running.

1. 1,2,3,4
2. 2,4,5,7
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 3,4,6,7
5. 2,3,4,6
Question : As a QuickTechie Inc developer, you need to execute two MapReduce ETL job named QT and QT.
And the Hadoop cluster is configured with the YARN (MRv2 and Fair Scheduler enabled). And you submit a job QT1,
so that only job QT1 is running which almost take 5 hours to finish. After 1 Hour, you submit another Job QT2.
now Job QT1 and Job QT2 are running at the same time. Select the correct statement the way Fair Scheduler handle these two jobs?

1. When Job QT2 gets submitted, it will get assigned tasks, while job QT1 continues to run with fewer tasks
2. When Job QT2 gets submitted, Job QT1 has to finish first, before job QT1 can gets scheduled.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. When Job QT1 gets submitted, it consumes all the task slots.
Question : Each node in your Hadoop cluster, running YARN,
has 64GB memory and 24 cores. Your yarn.site.xml has
the following configuration:

1. A
2. B
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. D
Question : YARN then provides processing capacity to each application by allocating Containers.
A Container is the basic unit of processing capacity in YARN, and is an encapsulation of resource elements

1. CPU
2. Memory
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Each Data Node of Hadoop Cluster