AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Professional Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : Acmeshell is trying to setting up a backup and restore system in AWS of their in premise system and needs HA and DR but is okay to have a longer
recovery time to save costs. Which of the below mentioned setup options helps achieve the objective of cost saving as well as DR in the most effective way?

1. Setup a small instance with AutoScaling; in case of DR start diverting all the load to AWS from on premise.
2. Replicate on premise DB to EC2 at regular intervals and setup a scenario similar to the pilot light.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Setup the backup data on S3 and transfer data to S3 regularly using the storage gateway.
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: AWS has many solutions for DR and HA. When the organization wants to have HA and DR but are okay to have a longer recovery time they should select the option backup and restore
with S3. The data can be sent to S3 using either Direct Connect, Storage Gateway or over the internet.
The EC2 instance will pick the data from the S3 bucket when started and setup the environment. This process takes longer but is very cost effective due to the low pricing of S3. In
all the other options, the EC2 instance might be running or there will be AMI storage costs.
Thus, it will be a costlier option. In this scenario the organization should plan appropriate tools to take a backup, plan the retention policy for data and setup security of the
data.
Question : Acmeshell.com is having an application which can start and stop an EC instance as per schedule and needs the MAC address of the instance
to be registered with its software. The instance is launched in EC2-CLASSIC. How can the organization update the MAC registration every time an instance is booted?

1. The instance MAC address never changes. Thus, it is not required to register the MAC address every time.
2. AWS never provides a MAC address to an instance; instead the instance ID is used for identifying the instance for any software registration.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Acmeshell should write a boot strapping script which will get the MAC address from the instance metadata and use that script to register with the application.
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Exp: Instance metadata is data about your instance that you can use to configure or manage the running instance. Instance metadata is divided into categories. For more information,
see Instance Metadata Categories. EC2 instances can also include dynamic data, such as an instance identity document that is generated when the instance is launched. For more
information, see Dynamic Data Categories.
You can also access the user data that you supplied when launching your instance. For example, you can specify parameters for configuring your instance, or attach a simple script.
You can also use this data to build more generic AMIs that can be modified by configuration files supplied at launch time. For example, if you run web servers for various small
businesses, they can all use the same AMI and retrieve their content from the Amazon S3 bucket you specify in the user data at launch. To add a new customer at any time, simply
create a bucket for the customer, add their content, and launch your AMI. If you launch more than one instance at the same time, the user data is available to all instances in that
reservation.
Because you can access instance metadata and user data from within your running instance, you do not need to use the Amazon EC2 console or the CLI tools. This can be helpful when
you're writing scripts to run from within your instance. For example, you can access your instance's local IP address from within the running instance to manage a connection to an
external application.
Important : Although you can only access instance metadata and user data from within the instance itself, the data is not protected by cryptographic methods. Anyone who can access
the instance can view its metadata. Therefore, you should take suitable precautions to protect sensitive data (such as long-lived encryption keys). You should not store sensitive
data, such as passwords, as user data. For more information about adding user data when you launch an instance, see Launching an Instance. You can add or modify user data on Amazon
EBS-backed instances when they're stopped. For more information about adding user data to a stopped instance, see Modifying a Stopped Instance.
When you are adding user data, take note of the following:
User data is treated as opaque data: what you give is what you get back. It is up to the instance to be able to interpret it.
User data is limited to 16 KB. This limit applies to the data in raw form, not base64-encoded form.
User data must be base64-encoded before being submitted to the API. The API command line tools perform the base64 encoding for you. The data is decoded before being presented to the instance. For more information about base64 encodings.
Question : QuickTechie.com is setting up a highly scalable application using the Elastic Beanstalk. The organization is using ELB as well as VPC with public and
private subnets. The organization wants that all the EC2 instances should have a private IP as well as receive data from ELB. Which of below mentioned requirements
will not be required while configuring this setup?

1. Configure ELB and NAT as a part of the public subnet only.
2. Launch the EC2 instances with only the public subnet.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Create routing rules which will route all outbound traffic from the EC2 instances through NAT.
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Exp: What VPC Configurations Do I Need?
When you use Amazon VPC with Elastic Beanstalk, you can launch Elastic Beanstalk resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances, in a public or private subnet. The subnets that you require
depend on your Elastic Beanstalk application environment type and whether the resources you launch are public or private. The following scenarios discuss sample VPC configurations
that you might use for a particular environment.
Single-instance environments
For single-instance environments, Elastic Beanstalk assigns an Elastic IP address (a static, public IP address) to the instance so that it can communicate directly with the
Internet. No additional network interface, such as a network address translator (NAT), is required for a single-instance environment.
If you have a single-instance environment without any associated private resources, such as a back-end Amazon RDS DB instance, create a VPC with one public subnet and include the
instance in that subnet. For more information, see Example: Launching a Single-Instance Environment without Any Associated Private Resources in a VPC.
If you have resources that you don't want public, create a VPC with one public subnet and one private subnet. Add all your public resources like the single Amazon EC2 instance in
the public subnet, and add private resources like a back-end Amazon RDS DB instance in the private subnet. If you do launch an Amazon RDS DB instance in a VPC, you must create at least two different private subnets that are in different Availability Zones (an Amazon RDS requirement).
Load-balancing, autoscaling environments
For load-balancing, autoscaling environments, you can either create a public and private subnet for your VPC or use a single public subnet. In the case of a load-balancing,
autoscaling environment with both a public and private subnet, Amazon EC2 instances in the private subnet require Internet connectivity. Consider the following scenarios.
If you want your Amazon EC2 instances to have a private IP address, create a public and private subnet for your VPC in each Availability Zone (an Elastic Beanstalk requirement).
Then add your public resources, like the load balancer and NAT, to the public subnet. That way, Elastic Beanstalk assigns them unique Elastic IP addresses (a static, public IP
address). Launch your Amazon EC2 instances in the private subnet so that Elastic Beanstalk assigns them nonrouteable private IP addresses.
Without a public IP address, an Amazon EC2 instance can't directly communicate with the Internet. Although Amazon EC2 instances in a private subnet can't send outbound traffic by
default, neither can they receive unsolicited inbound connections from the Internet.
To enable communication between the private subnet and the public subnet and the Internet beyond the public subnet, create routing rules that do the following:
Route all inbound traffic to an Amazon EC2 instance through a load balancer.
Route all outbound traffic from an Amazon EC2 instance through a NAT.The Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) allows the user to define a virtual networking environment
in a private, isolated section of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. The user has complete control over the virtual networking environment. If the organization wants the
Amazon EC2 instances to have a private IP address, he should create a public and private subnet for VPC in each Availability Zone (this is an AWS Elastic Beanstalk
requirement). The organization should add their public resources, such as ELB and NAT to the public subnet and accordingly, AWS Elastic Beanstalk assigns them unique elastic
IP addresses (a static, public IP address). The organization should launch Amazon EC2 instances in a private subnet so that AWS Elastic Beanstalk assigns them non-routable
private IP addresses. Now the organization should configure route tables with the following rules:
" route all inbound traffic from ELB to EC2 instances
" route all outbound traffic from EC2 instances through NAT
Related Questions
Question : You have created a subnet and specified the CIDR block .../ for subnet. Please select the correct statement

1. It supports 24 IP addresses, You can break this CIDR block into two subnets, each supporting 12 IP addresses
2. It supports 128 IP addresses, You can break this CIDR block into two subnets, each supporting 64 IP addresses
3. It supports 256 IP addresses, You can break this CIDR block into two subnets, each supporting 128 IP addresses
4. It supports 24 IP addresses, You can not break this CIDR block into two subnets
Question : In the given diagram,
the route table associated with subnet 1 routes
all traffic __________ to an Internet
gateway (for example, igw-1a2b3c4d).
Because instance V1 has an Elastic IP address,
it can be reached from the Internet.
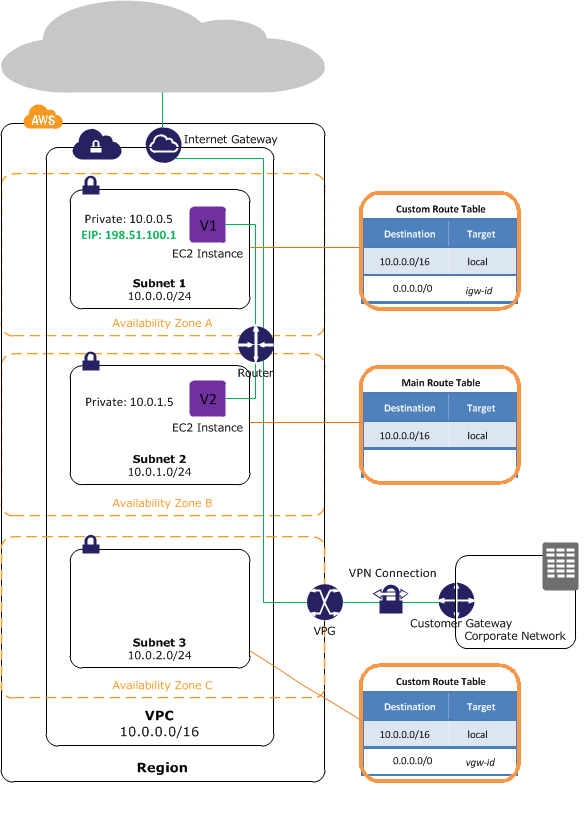
1. (0.0.0.16/0)
2. (0.0.0.24/0)
3. (0.0.0.0/0)
4. (0.0.0.5/0)
Question : QuickTechie.com is planning to implement a scalable web application with AWS EC to achieve HA with multi AZ features. The application requires an
Weblogic J2EE app server and may require a load which will be catered by 2 large instances. Select the configurations is better choice for HA in DR

1. Launch only one large instance and setup Auto Scaling with ELB.
2. Launch two large instances in separate AZs and load balance them with ELB.
3. Launch 8 small EC2 instances with two instances in each zone for better HA and DR and load balance each with ELB.
4. Launch 4 small instances in separate AZs and load balance them with ELB.
Question : You have created a Subnet where all your app servers instances will be launched and the database remain in the local data center. Also you have
created VPN for having communication between your dataceneter and VPC subnets. Now you wish to provide security on instance level under a subnet. Which one
from the below feature will help you to implement the same.

1. Restricting the port 80 and 8080 for outbound traffic.
2. security groups will help
3. Network ACL will help
4. 1 and 3 both needs to be implemented
Question : You are running QuickTechie.com website using servers, ( servers in different data centeres , where is active and is passive).
Now you want to configure DNS such that whenever request for website comes and if any of the active server is available out of 5 active it should not return
the IP address of Passive servers. Which of the following configuration will help implmenting it..

1. Amazon Route 53 , Active-active failover
2. Amazon Route 53 , Active-passive failover
3. Amazon Route 53 , Passive-passive failover
4. Amazon Route 53 ,Active-active-passive
5. Any of the above
Question : QuickTechie.com is setting up Oracle RDS for their applications and wants to secure Oracle RDS access with VPC.
Which of the following options is not required while designing the Oracle RDS with VPC?

1. If the QuickTechie.com Inc is connecting RDS from the internet it must enable the VPC attributes DNS hostnames and DNS resolution.
2. The QuickTechie.com Inc must create a subnet group with public and private subnets. Both the subnets can be in the same or separate AZ.
3. The QuickTechie.com Inc must create a subnet group with VPC using more than one subnets which are a part of separate AZs.
4. The QuickTechie.com Inc should keep minimum one IP address in each subnet reserved for RDS failover.