Oracle Java Programming Certification Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : Which three statements describe the object-oriented features of the Java language?
A. objects cannot be reused.
B. A subclass can inherit from a superclass.
C. objects can share behaviors with other objects.
D. A package must contain more than one class.
E. object is the root class of all other objects.
F. A main method must be declared in every class.

1. A,B,D
2. B,C,E
3. A,C,F
4. B,C,F
Correct Answer : 2
Explanation:
once, you create an object of a class and you can use it as many time as it is needed or until destroyed.
public class Test{
public void method1();
public void method2();
public static void main(String args[]){
Test t1 = new Test();
t1.method1();
t1.method2();
}
}
We have used same object t1 twice.
You can call method of another objects, if you have refrence to that object. Hence, yes behaviors can be shared.
No it is not necessary to package have a class. Package can contain 0 to n number of classes.
Question : Given:
And given the commands:
javac Test.Java
Java Test Hello
What is the result?

1. Success
2. Failure
3. Compilation fails.
4. Anexception is thrown at runtime
Correct Answer : 2
Explanation: Here, we have used ternary operators.
("Hello".equals("Hello")) ? false : true;
Both the string are same , hence condition is true. Which will return false. Hence, code will go into else block which will print "Failure"
Program will run perfectly and prints the "Failure"
Question : Given the code fragment
public static void main(String[] args) {
double discount = 0;
int qty = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
//line n1
}
And given the requirements:
- If the value of the qty variable is greater than or equal to 90, discount = 0.5
- If the value of the qty variable is between 80 and 90, discount = 0.2
Which two code fragments can be independently placed at line n1 to meet the requirements?

1. A,C
2. B,C
3. C,D
4. D,E
Correct Answer : 1
Related Questions
Question : Which three are advantages of the Java exception mechanism?
A. Improves the program structure because the error handling code is separated from the normal program function
B. Provides a set of standard exceptions that covers all the possible errors
C. Improves the program structure because the programmer can choose where to handle exceptions
D. Improves the program structure because exceptions must be handled in the method in which they occurred
E. Allows the creation of new exceptions that are tailored to the particular program being created

1. A,B,C
2. B,D,E
3. A,C,D
4. B,C,E
Exp : A program can use exceptions to indicate that an error occurred. To throw an exception, use the throw statement and provide it with an exception object - a descendant of
Throwable - to provide information about the specific error that occurred. A method that throws an uncaught, checked exception must include a throws clause in its declaration.
A program can catch exceptions by using a combination of the try, catch, and finally blocks.
The try block identifies a block of code in which an exception can occur.
The catch block identifies a block of code, known as an exception handler, that can handle a particular type of exception.
The finally block identifies a block of code that is guaranteed to execute, and is the right place to close files, recover resources, and otherwise clean up after the code enclosed
in the try block.
The try statement should contain at least one catch block or a finally block and may have multiple catch blocks.
The class of the exception object indicates the type of exception thrown. The exception object can contain further information about the error, including an error message. With exception chaining, an exception can point to the exception that caused it, which can in turn point to the exception that caused it, and so on.
Advantage 1: Separating Error-Handling Code from "Regular" Code
Advantage 2: Propagating Errors Up the Call Stack
Advantage 3: Grouping and Differentiating Error Types
Question : Given the code fragment: What is the result?
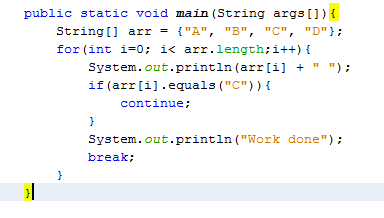
1. A B C Work done
2. A B C D Work done
3. A Work done
4. Compilation fails
Question : Given the code fragment:
Which code fragment, when inserted at line 3, enables the code to print 10:20?
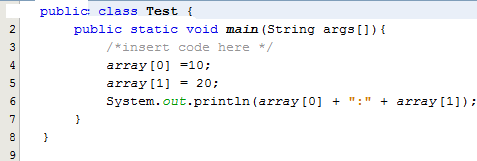
1. int[] array n= new int[2];
2. int[] array;
array = int[2];
3. int array = new int[2];
4. int array [2] ;
Question : Given:
What is the result?

1. 3 4 5 6
2. 3 4 3 6
3. 5 4 5 6
4. 3 6 4 6
Question : Given: What is the result?

1. C B A
2. C
3. A B C
4. Compilation fails at line n1 and line n2
Question : Given the code fragment:
What is the result?

1. [Robb, Rick, Bran]
2. [Robb, Rick]
3. [Robb, Bran, Rick, Bran]
4. An exception is thrown at runtime.
Question :
1. Replace line n2 with
e.name="Joe";
e.contract=true;
e.salary=100;
2. Replace line n2 with
this.name="Joe";
this.contract=true;
this.salary=100;
3. Replace line n1 with
this.name=new String("Joe");
this.contract=new Boolean(true);
this.salary=new Double(100);
4. Replace line n1 with
name="Joe";
contract=TRUE;
salary=.0f;
5. Replace line n1 with
this("Joe", true, 100);

1. 1,2
2. 1,3
3. 2,4
4. 4,5
5. 3,5