Cloudera Databricks Data Science Certification Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : Which of the following is/are superviswed learning algorithm

1. Logistic regression
2. Naive Bayes classifier
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Only 1 and 2
5. All 1,2 and 3
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Linear classifiers
Fisher's linear discriminant
Logistic regression
Multinomial logistic regression
Naive Bayes classifier
Perceptron
Support vector machines
Question : Which of the following is a unsupervided learning algorithms
1. K-means algorithm
2. k-nearest neighbor
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Hierarchical clustering
5. Logistic regression

1. 1,2,3,4
2. 1,3,4,5
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 1,3,5
5. 2,3,4
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Unsupervised learning
Hierarchical clustering
Single-linkage clustering
Conceptual clustering
Cluster analysis
K-means algorithm
Fuzzy clustering
DBSCAN
OPTICS algorithm
Question : Select the correct algorithm which represent supervised learning?

1. PCA
2. SVD
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Logistic regression
5. None of the above
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
In supervised systems, the data as presented to a machine learning algorithm is fully labelled. That means: all examples are presented with a classification that the machine is meant to reproduce. For this, a classifier is learned from the data, the process of assigning labels to ye unseen instances is called classifi- cation.
Unsupervised systems are not provided any training examples at all and conduct clustering. This is the division of data instances into several groups. The results of clustering algorithms are data driven, hence more 'natural' and better suited to the underlying structure of the data. This advantage is also its major drawback: without a possibility to tell the machine what to do (like in classification), it is difficult to judge the quality of clustering results in a conclusive way. But the absence of training example preparation makes the unsupervised paradigm very appealing
In supervised learning means Labeled Data , which is to be learned for examples in a test set.
k-means clustering operates on unlabeled data. Both the Principal Component Analysis
and the Singular Value Decomposition also operate on unlabeled data
and are concerned with finding latent structure in data rather than predicting labels.
Expectation Maximization concerns finding most-likely parameter values for a model.
Related Questions
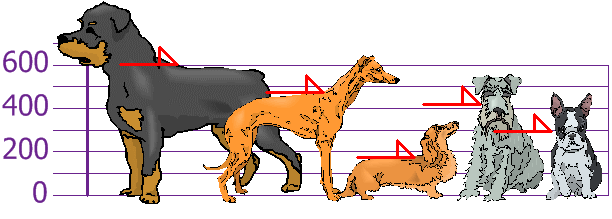
Question : You and your friends have just measured the heights of your dogs (in millimetres):
The heights (at the shoulders) are: 600mm, 470mm, 170mm, 430mm and 300mm.
Find out the Variance
1. 2000
2. 20000
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Not enough information to calculate the mean
Question : You and your friends have just measured the heights of your dogs (in millimetres):
The heights (at the shoulders) are: 600mm, 470mm, 170mm, 430mm and 300mm.
Find out the Standard Deviation

1. 147
2. 140
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Not enough information to calculate the mean
Question :
You have following data in a hive table
ID:INT,COLOR:TEXT,WIDTH:INT
1,green,190
2,blue,300
3,yellow,220
4,blue,199
5,green,199
6,yellow,299
7,green,799
Select the correct Mapper and Reducer which
can produce the output similar to following queries
Select id,color,width from table where width >=200;

1. 1
2. 2
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 4
Question :
You have following data in a hive table
ID:INT,COLOR:TEXT,WIDTH:INT
1,green,190
2,blue,300
3,yellow,220
4,blue,199
5,green,199
6,yellow,299
7,green,799
After running thje following MapReduce program, what output it will produces as first line.

1. 1,green,190
2. 4,blue,199
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. it will through java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Question :
You have following data in a hive table
ID:INT,COLOR:TEXT,WIDTH:INT
1,green,190
2,blue,300
3,yellow,220
4,blue,199
5,green,199
6,yellow,299
7,green,799
Select the correct MapReduce program
which can produce the output similar
to below Hive Query.
Select color from table where width >=220;

1. 1
2. 2
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 4
Question :
You have following data in a hive table
ID:INT,COLOR:TEXT,WIDTH:INT
1,green,190
2,blue,300
3,yellow,220
4,blue,199
5,green,199
6,yellow,299
7,green,799
Select the correct MapReduce program which
can produce the output similar to below Hive Query.
Select id,color from table where width >=220;

1. 1
2. 2
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 4