AWS Certified Solutions Architect - Professional Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : An ERP application is deployed in multiple Availability Zones in a single region. In the event of failure, the RTO must be less than hours, and the
RPO is 15 minutes. The customer realizes that data corruption occurred roughly 1.5 hours ago. Which DR strategy can be used to achieve this RTO and RPO in the event
of this kind of failure?

1. Take 15-minute DB backups stored in Amazon Glacier, with transaction logs stored in Amazon S3 every 5 minutes.
2. Use synchronous database master-slave replication between two Availability Zones.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Take hourly DB backups to an Amazon EC2 instance store volume, with transaction logs stored in Amazon S3 every 5 minutes.
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: Glacier takes too long to restore
Replication won't let you go back in time
Instance store is ephermal . Not to mention Glacier restore alone will take 3-5 hours, and then add on the time it will take to restore that from the temporary restored object in
S3 (if you archived it using a S3 lifecycle policy)
I actually think it's C. VTL would take too long, so it's not D. Glacier would take too long, so it's not B. Because the question is best RTO, I think C would be best, as you
wouldn't have to wait to create a EBS volume from a snapshot (this does take a little time), and could just mount the SGway volume via iSCSI.
Very close between A and C though, kinda tricky.
Question : QuickTechie.com is having a VPC for the Billing team, and another VPC for the Risk Team. The Billing team team requires access to all the instances
running in the Risk Team VPC while the Risk Team requires access to all the resources in the Billing Team. How can the QuickTechie.com setup this scenario?

1. Setup ACL with both VPCs which will allow traffic from the CIDR of the other VPC.
2. Setup VPC peering between the VPCs of Risk Team and Billing Team.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Setup the security group with each VPC which allows traffic from the CIDR of another VPC
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IP addresses. Instances in either VPC can
communicate with each other as if they are within the same network. You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs, or with a VPC in another AWS account within a
single region.
AWS uses the existing infrastructure of a VPC to create a VPC peering connection; it is neither a gateway nor a VPN connection, and does not rely on a separate piece of physical
hardware. There is no single point of failure for communication or a bandwidth bottleneck.
A VPC peering connection can help you to facilitate the transfer of data; for example, if you have more than one AWS account, you can peer the VPCs across those accounts to create a
file sharing network. You can also use a VPC peering connection to allow other VPCs to access resources you have in one of your VPCs.
o establish a VPC peering connection, the owner of the requester VPC (or local VPC) sends a request to the owner of the peer VPC to create the VPC peering connection. The peer VPC
can be owned by you, or another AWS account, and cannot have a CIDR block that overlaps with the requester VPC's CIDR block. The owner of the peer VPC has to accept the VPC peering
connection request to activate the VPC peering connection. To enable the flow of traffic between the peer VPCs using private IP addresses, add a route to one or more of your VPC's
route tables that points to the IP address range of the peer VPC. The owner of the peer VPC adds a route to one of their VPC's route tables that points to the IP address range of
your VPC. You may also need to update the security group rules that are associated with your instance to ensure that traffic to and from the peer VPC is not restricted. For more
information about security groups, see Security Groups for Your VPC.
A VPC peering connection is a one to one relationship between two VPCs. You can create multiple VPC peering connections for each VPC that you own, but transitive peering
relationships are not supported: you will not have any peering relationship with VPCs that your VPC is not directly peered with.
Question : VPC Peering Connection Lifecycle, please fill in the exception scenerio marked in red.
1. Failed
2. Expired
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Deleted
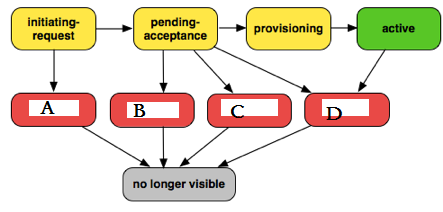
1. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
2. A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Explanation: A VPC peering connection goes through various stages starting from when the request is initiated. At each stage, there may be actions that you can take, and at the end of its
lifecycle, the VPC peering connection remains visible in the VPC console and API or command line output for a period of time.
Initiating-request: A request for a VPC peering connection has been initiated. At this stage, the peering connection may fail or may go to pending-acceptance.
Failed: The request for the VPC peering connection has failed. During this state, it cannot be accepted or rejected. The failed VPC peering connection remains visible to the
requester for 2 hours.
Pending-acceptance: The VPC peering connection request is awaiting acceptance from the owner of the peer VPC. During this state, the owner of the requester VPC can delete the
request, and the owner of the peer VPC can accept or reject the request. If no action is taken on the request, it will expire after 7 days.
Expired: The VPC peering connection request has expired, and no action can be taken on it by either VPC owner. The expired VPC peering connection remains visible to both VPC
owners for 2 days.
Rejected: The owner of the peer VPC has rejected a pending-acceptance VPC peering connection request. During this state, the request cannot be accepted. The rejected VPC peering
connection remains visible to the owner of the requester VPC for 2 days, and visible to the owner of the peer VPC for 2 hours. If the request was created within the same AWS
account, the rejected request remains visible for 2 hours.
Provisioning: The VPC peering connection request has been accepted, and will soon be in the active state.
Active: The VPC peering connection is active. During this state, either of the VPC owners can delete the VPC peering connection, but cannot reject it.
Deleted: An active VPC peering connection has been deleted by either of the VPC owners, or a pending-acceptance VPC peering connection request has been deleted by the owner of
the requester VPC. During this state, the VPC peering connection cannot be accepted or rejected. The VPC peering connection remains visible to the party that deleted it for 2
hours, and visible to the other party for 2 days. If the VPC peering connection was created within the same AWS account, the deleted request remains visible for 2 hours.
Related Questions
Question : An AWS customer is deploying an application that is composed of an AutoScaling group of EC Instances. The customers security policy requires that every outbound
connection from these instances to any other service within the customers Virtual Private Cloud must be authenticated using a unique x 509 certificate that contains the specific
instance-id. In addition an x 509 certificates must be signed by the customer's Key management service in order to be trusted for authentication.
Which of the following configurations will support these requirements?

1. Configure an IAM Role that grants access to an Amazon S3 object containing a signed certificate and configure the Auto Scaling group to launch instances with this
role. Have the instances bootstrap get the certificate from Amazon S3 upon first boot.
2. Embed a certificate into the Amazon Machine Image that is used by the Auto Scaling group. Have the launched instances generate a certificate signature request with
the instance's assigned instance-id to the Key management service for signature.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
generate a signed certificate and send it directly to the newly launched instance.
4. Configure the launched instances to generate a new certificate upon first boot. Have the Key management service poll the AutoScaling group for associated instances and
send new instances a certificate signature that contains the specific instance-id.
Question : You are designing a photo sharing mobile app the application will store all pictures in a single Amazon S bucket. Users will upload pictures from their mobile device
directly to Amazon S3 and will be able to view and download their own pictures directly from Amazon S3. You want to configure security to handle potentially millions of users in the
most secure manner possible. What should your server-side application do when a new user registers on the photo-sharing mobile application?

1. Create a set of long-term credentials using AWS Security Token Service with appropriate permissions. Store these credentials in the mobile app and use them to access
Amazon S3.
2. Record the user's Information in Amazon RDS and create a role in IAM with appropriate permissions. When the user uses their mobile app create temporary credentials
using the AWS Security Token Service 'AssumeRole' function Store these credentials in the mobile app's memory and use them to access Amazon S3. Generate new credentials the next time
the user runs the mobile app.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
permissions. Store these credentials in the mobile app's memory and use them to access Amazon S3. Generate new credentials the next time the user runs the mobile app.
4. Create IAM user. Assign appropriate permissions to the IAM user. Generate an access key and secret key for the IAM user, store them in the mobile app and use these
credentials to access Amazon S3.
5. Create an IAM user. Update the bucket policy with appropriate permissions for the IAM user Generate an access Key and secret Key for the IAM user, store them In the
mobile app and use these credentials to access Amazon S3.
Question : A web-startup runs its very successful social news application on Amazon EC with an Elastic Load Balancer, an Auto-Scaling group of Java/Tomcat application-servers,
and DynamoDB as data store. The main web-application best runs on m2 x large instances since it is highly memory- bound. Each new deployment requires semi-automated creation
and testing of a new AMI for the application servers which takes quite a while and is therefore only done once per week. Recently, a new chat feature has been implemented in nodejs
and needs to be integrated in the architecture. First tests show that the new component is CPU bound. Because the company has some experience with using Chef, they decided to
streamline the deployment process and use AWS Ops Works as an application life cycle tool to simplify management of the application and reduce the deployment cycles.
What configuration in AWS Ops Works is necessary to integrate the new chat module in the most cost-efficient and flexible way?

1. Create one AWS Ops Works stack, create one AWS Ops Works layer, create one custom recipe
2. Create one AWS Ops Works stack, create two AWS Ops Works layers create one custom recipe
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Create two AWS Ops Works stacks, create two AWS Ops Works layers create two custom recipe
Question : You are tasked with moving a legacy application from a virtual machine running Inside your datacenter to an Amazon VPC. Unfortunately this app requires access to a
number of on-premises services and no one who configured the app still works for your company. Even worse there's no documentation for it. What will allow the application running
inside the VPC to reach back and access its internal dependencies without being reconfigured?
(Choose 3 answers)
A. An AWS Direct Connect link between the VPC and the network housing the internal services.
B. An Internet Gateway to allow a VPN connection.
C. An Elastic IP address on the VPC instance
D. An IP address space that does not conflict with the one on-premises
E. Entries in Amazon Route 53 that allow the Instance to resolve its dependencies IP addresses
F. A VM Import of the current virtual machine

1. A,B,C
2. C,D,E
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. A,D,F
Question : Your system recently experienced down time during the troubleshooting process. You found that a new administrator mistakenly terminated several production EC
instances. Which of the following strategies will help prevent a similar situation in the future?
The administrator still must be able to:
- launch, start stop, and terminate development resources.
- launch and start production instances.

1. Create an IAM user, which is not allowed to terminate instances by leveraging production EC2 termination protection.
2. Leverage resource based tagging along with an IAM user, which can prevent specific users from terminating production EC2 resources.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Create an IAM user and apply an IAM role which prevents users from terminating production EC2 instances.
Question : Your fortune company has under taken a TCO (total cost of ownership) analysis evaluating the use of Amazon S versus acquiring more hardware. The outcome was that
all employees would be granted access to use Amazon S3 for storage of their personal documents. Which of the following will you need to consider so you can set up a solution that