IBM Certified Data Architect - Big Data Certification Questions and Answers (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : What describes the relationship between MapReduce and Hive?

1. Hive provides additional capabilities that allow certain types of data manipulation not possible with MapReduce.
2. Hive programs rely on MapReduce but are extensible, allowing developers to do special-purpose processing not provided by MapReduce.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Hive provides no additional capabilities to MapReduce. Hive programs are executed as MapReduce jobs via the Hive interpreter.
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Hive is a framework that translates queries written in Hive QL into jobs that are executed by the MapReduce framework. Hive does not provide any functionality that isn't provided
by MapReduce, but it makes some types of data operations significantly easier to perform.
Question : What is HIVE?

1. HIVE is part of the Apache Hadoop project that enables in-memory analysis of real-time streams of data
2. Hive is a way to add data from local file system to HDFS
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Hive is a part of the Apache Hadoop project that provides SQL like interface for data processing
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Hive is a project initially developed by facebook specifically for people with very strong SQL skills and not very strong Java skills who want to query data in Hadoop
Question : Which statement is true about apache Hadoop ?

1. HDFS performs best with a modest number of large files
2. No Randome Writes is alowed to the file
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. All of the above
Correct Answer : Get Lastest Questions and Answer :
Related Questions
Question : IBM Cloudant is a managed NoSQL database service that moves application data closer to all the places it needs to be

1. True
2. False
Question : Which of the following is IBM NoSQL Fully managed DBaaS (database-as-a-service) tool?

1. Cloudant
2. HBase
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. DB2
Question : Which of the following is true about Cloudant?

1. IBM Cloudant is a Fully managed DBaaS
2. Cloudant indexing is flexible and powerful, and includes real-time MapReduce, Apache Lucene-based full-text search, advanced Geospatial, and declaritive
Cloudant Query.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 1 and 2
5. 1,2 and 3
Question : What occurs when you run a Hadoop job, specifying an output directory job output which already exists in HDFS?

1. An error will occur immediately, because the output directory must not already exist when a MapReduce job commences.
2. An error will occur after the Mappers have completed but before any Reducers begin to run, because the output path must not exist when the Reducers commence.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. The job will run successfully. Output from the Reducers will overwrite the contents of the existing directory.
Ans : 1
Exp : When a job is run, one of the first things done on the client is a check to ensure that the output directory does not already exist. If it does, the client will immediately
terminate. The job will not be submitted to the cluster; the check takes place on the client.
Question : Select the correct statement for OOzie workflow

1. OOzie workflow runs on a server which is typically outside of Hadoop Cluster
2. OOzie workflow definition are submitted via HTTP.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. All 1,2 and 3 are correct
5. Only 1 and 3 are correct
Ans : 4
Exp : Check the URL http://oozie.apache.org/docs/3.1.3-incubating/WorkflowFunctionalSpec.html
Question : What is the result when you execute: hadoop jar SampleJar.jar MyClass on a client machine?

1. SampleJar.jar is placed in a temporary directory in HDFS
2. An error will occur, because you have not provided input and output directories
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. SampleJar.jar is sent directly to the JobTracker
Ans : 1
Exp : When a job is submitted to the cluster, it is placed in a temporary directory in HDFS and the JobTracker is notified of that location. The configuration for the job is
serialized to an XML file, which is also placed in a directory in HDFS. Some jobs require you to specify the input and output directories on the command line, but this is not a
Hadoop requirement.
Question : During a MapReduce v(MRv) job submission, there are a number of steps between the ResourceManager
receiving the job submission and the map tasks running on different nodes.
1. Order the following steps according to the flow of job submission in a YARN cluster:
2. The ResourceManager application manager asks a NodeManager to launch the ApplicationMaster
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. The ApplicationMaster sends a request to the assigned NodeManagers to run the map tasks
5. The ResourceManager scheduler allocates a container for the ApplicationMaster
6. The ApplicationMaster determines the number of map tasks based on the input splits
7. The ResourceManager scheduler makes a decision where to run the map tasks based on the memory requirements and data locality

1. 3,4,6,5,1,2
2. 2,3,4,5,6,1
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 3,4,6,5,1,2
5. 6,5,3,4,1,2
Ans : 2
Exp : Link : http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.3.0/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html
MapReduce has undergone a complete overhaul in hadoop-0.23 and we now have, what we call, MapReduce 2.0 (MRv2) or YARN.
The fundamental idea of MRv2 is to split up the two major functionalities of the JobTracker, resource management and job scheduling/monitoring, into separate daemons. The idea is
to have a global ResourceManager (RM) and per-application ApplicationMaster (AM). An application is either a single job in the classical sense of Map-Reduce jobs or a DAG of jobs.
The ResourceManager and per-node slave, the NodeManager (NM), form the data-computation framework. The ResourceManager is the ultimate authority that arbitrates resources among all
the applications in the system.
The per-application ApplicationMaster is, in effect, a framework specific library and is tasked with negotiating resources from the ResourceManager and working with the
NodeManager(s) to execute and monitor the tasks.
The ResourceManager has two main components: Scheduler and ApplicationsManager.
The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to familiar constraints of capacities, queues etc. The Scheduler is pure scheduler
in the sense that it performs no monitoring or tracking of status for the application. Also, it offers no guarantees about restarting failed tasks either due to application failure
or hardware failures. The Scheduler performs its scheduling function based the resource requirements of the applications; it does so based on the abstract notion of a resource
Container which incorporates elements such as memory, cpu, disk, network etc. In the first version, only memory is supported.
The Scheduler has a pluggable policy plug-in, which is responsible for partitioning the cluster resources among the various queues, applications etc. The current Map-Reduce
schedulers such as the CapacityScheduler and the FairScheduler would be some examples of the plug-in.
The CapacityScheduler supports hierarchical queues to allow for more predictable sharing of cluster resources
The ApplicationsManager is responsible for accepting job-submissions, negotiating the first container for executing the application specific ApplicationMaster and provides the
service for restarting the ApplicationMaster container on failure.
The NodeManager is the per-machine framework agent who is responsible for containers, monitoring their resource usage (cpu, memory, disk, network) and reporting the same to the
ResourceManager/Scheduler.
The per-application ApplicationMaster has the responsibility of negotiating appropriate resource containers from the Scheduler, tracking their status and monitoring for progress.
MRV2 maintains API compatibility with previous stable release (hadoop-0.20.205). This means that all Map-Reduce jobs should still run unchanged on top of MRv2 with just a recompile.
Question : You decide to create a cluster which runs HDFS in High Availability mode with automatic failover, using Quorum-based Storage.
Which service keeps track of which NameNode is active at any given moment?

1. YARN ResourceManager
2. Secondary NameNode
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. ZooKeeper
5. Individual JournalNode daemons
Ans : 4
Exp : When the first NameNode is started, it connects to ZooKeeper and registers itself as the Active NameNode. The next NameNode then sees that information and sets itself up in
Standby mode (in fact, the ZooKeeper Failover Controller is the software responsible for the actual communication with ZooKeeper). Clients never connect to ZooKeeper to discover
anything about the NameNodes. In an HDFS HA scenario, ZooKeeper is not used to keep track of filesystem changes. That is the job of the Quorum Journal Manager daemons.
Question : Which two daemons typically run on each slave node in a Hadoop cluster running MapReduce v (MRv) on YARN?
1. TaskTracker
2. Secondary NameNode
3. NodeManager
4. DataNode
5. ZooKeeper
6. JobTracker
7. NameNode
8. JournalNode

1. 1,2
2. 2,3
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 5,6
4. 7,8
Question : What happens under YARN if a Mapper on one node hangs while running a MapReduce job?

1. After a period of time, the ResourceManager will mark the map task attempt as failed and ask the NodeManager to terminate the container for the Map task
2. After a period of time, the NodeManager will mark the map task attempt as failed and ask the ApplicationMaster to terminate the container for the Map task
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. After a period of time, the ApplicationMaster will mark the map task attempt as failed and ask the NodeManager to terminate the container for the Map task
Question
What happens when you run the below job twice , having each input directory as one of the data file called data.csv.
with following command. Assuming there were no output directory exist
hadoop job HadoopExam.jar HadoopExam inputdata_1 output
hadoop job HadoopExam.jar HadoopExam inputdata_2 output
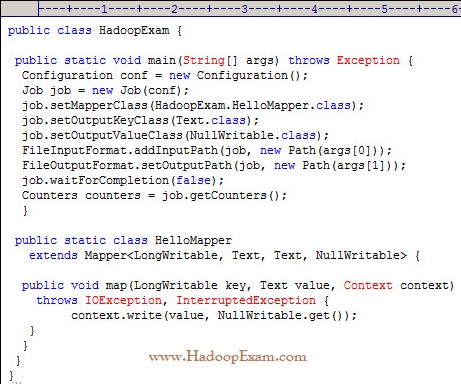
1. Both the job will write the output to output directory and output will be appended
2. Both the job will fail, saying output directory does not exist.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Both the job will successfully completes and second job will overwrite the output of first.
Ans : 3
Exp : First job will successfully run and second one will fail, because, if (output directory already exist then it will not run
and throws exception, complaining output directory already exist.
Question : Which of the following model can help you to visually represent that how an organization delivers value to its customers or beneficiaries ?

1. Business Model
2. Operational Model
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Logical Model
5. Physical Model