Cloudera Hadoop Administrator Certification Certification Questions and Answer (Dumps and Practice Questions)
Question : As a general recommendation, allowing for ______ Containers per disk and per core gives the best balance for cluster utilization.

1. One
2. Two
3. Three
4. Four
Correct Answer : 2
Explanation: resources. As a general recommendation, allowing for two Containers per disk and per core gives the best balance for cluster utilization.
When determining the appropriate YARN and MapReduce memory configurations for a cluster node, start with the available hardware resources. Specifically, note the following values on each node:
RAM (Amount of memory)
CORES (Number of CPU cores)
DISKS (Number of disks)
The total available RAM for YARN and MapReduce should take into account the Reserved Memory. Reserved Memory is the RAM needed by system processes and other Hadoop processes (such as HBase).
Reserved Memory = Reserved for stack memory + Reserved for HBase Memory (If HBase is on the same node)
Use the following table to determine the Reserved Memory per node.
Question : In the Hadoop . framework, if HBase is also running on the same node for which available RAM is GB, so what is the ideal configuration
for "Reserved System Memory"

1. 1GB
2. 2GB
3. 3GB
4. No need to reserve
Correct Answer : 1
The total available RAM for YARN and MapReduce should take into account the Reserved Memory. Reserved Memory is the RAM needed by system processes and other Hadoop processes (such as HBase).
Reserved Memory = Reserved for stack memory + Reserved for HBase Memory (If HBase is on the same node)
Use the following table to determine the Reserved Memory per node.
Reserved Memory Recommendations
Total Memory per Node Recommended Reserved System Memory Recommended Reserved HBase Memory
4 GB 1 GB 1 GB
8 GB 2 GB 1 GB
16 GB 2 GB 2 GB
24 GB 4 GB 4 GB
48 GB 6 GB 8 GB
64 GB 8 GB 8 GB
72 GB 8 GB 8 GB
96 GB 12 GB 16 GB
128 GB 24 GB 24 GB
256 GB 32 GB 32 GB
512 GB 64 GB 64 GB
Question : The next calculation is to determine the maximum number of containers allowed per node. The following formula can be used:
# of containers = min (2*CORES, 1.8*DISKS, (Total available RAM) / MIN_CONTAINER_SIZE)
Where MIN_CONTAINER_SIZE is the minimum container size (in RAM). This value is dependent on the amount of RAM available -- in smaller memory nodes, the minimum container size should also be smaller
Available Total RAM per Node"is 24GB, then what is the "Recommended Minimum Container Size"

1. 256MB
2. 512MB
3. 1024MB
4. 2048 MB
Correct Answer : 4
The next calculation is to determine the maximum number of containers allowed per node. The following formula can be used:
# of containers = min (2*CORES, 1.8*DISKS, (Total available RAM) / MIN_CONTAINER_SIZE)
Where MIN_CONTAINER_SIZE is the minimum container size (in RAM). This value is dependent on the amount of RAM available -- in smaller memory nodes, the minimum container size should also be smaller. The following table outlines the recommended values:
Total RAM per Node Recommended Minimum Container Size
Less than 4 GB 256 MB
Between 4 GB and 8 GB 512 MB
Between 8 GB and 24 GB 1024 MB
Above 24 GB 2048 MB
Related Questions
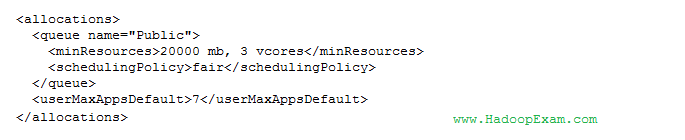
Question : You have GB of memory available in your cluster. The cluster's memory is shared between
three different queues: public, manager and analyst. The following configuration file is also in place:
A job submitted to the public queue requires 10 GB, a job submitted to the maanger queue requires 30 GB,
and a job submitted to the analyst queue requires 25 GB. Given the above configuration,
how will the Fair Scheduler allocate resources for each queue?
1. 40 GB for Public queue, 0 GB for Manager queue and 0 GB for Analyst queue
2. 10 GB for Public queue, 30 GB for Manager queue and 0 GB for Analyst queue
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 20 GB for the Public queue, 10 GB for the Manager queue, and 10 GB for the Analyst queue
Question : You have configured the Fair Scheduler on your Hadoop cluster. You submit a Equity job so that ONLY job Equity is
running on the cluster. Equity Job requires more task resources than are available simultaneously on the cluster. Later you submit ETF job.
Now Equity and ETF are running on the cluster at the same time.
Identify aspects of how the Fair Scheduler will arbitrate cluster resources for these two jobs?
1. When job ETF gets submitted, it will be allocated task resources, while job Equity continues to run with fewer task resources available to it.
2. When job Equity gets submitted, it consumes all the task resources available on the cluster.
3. When job ETF gets submitted, job Equity has to finish first, before job ETF can be scheduled.
4. When job Equity gets submitted, it is not allowed to consume all the task resources on the cluster in case another job is submitted later.

1. 1,2,3
2. 2,3
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 1,2,4
5. 1,2
Question : In the QuickTechie Inc. you have upgraded your Hadoop Cluster to MRv and in which you are
going to user FairScheduler. Using this scheduler you will which of the following benefit.
1. Run jobs at periodic times of the day.
2. Ensure data locality by ordering map tasks so that they run on data local map slots
3. Reduce job latencies in an environment with multiple jobs of different sizes.
4. Allow multiple users to share clusters in a predictable, policy-guided manner.
5. Reduce the total amount of computation necessary to complete a job.
6. Support the implementation of service-level agreements for multiple cluster users.
7. Allow short jobs to complete even when large, long jobs (consuming a lot of resources) are running.

1. 1,2,3,4
2. 2,4,5,7
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. 3,4,6,7
5. 2,3,4,6
Question : As a QuickTechie Inc developer, you need to execute two MapReduce ETL job named QT and QT.
And the Hadoop cluster is configured with the YARN (MRv2 and Fair Scheduler enabled). And you submit a job QT1,
so that only job QT1 is running which almost take 5 hours to finish. After 1 Hour, you submit another Job QT2.
now Job QT1 and Job QT2 are running at the same time. Select the correct statement the way Fair Scheduler handle these two jobs?

1. When Job QT2 gets submitted, it will get assigned tasks, while job QT1 continues to run with fewer tasks
2. When Job QT2 gets submitted, Job QT1 has to finish first, before job QT1 can gets scheduled.
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. When Job QT1 gets submitted, it consumes all the task slots.
Question : Each node in your Hadoop cluster, running YARN,
has 64GB memory and 24 cores. Your yarn.site.xml has
the following configuration:

1. A
2. B
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. D
Question : YARN then provides processing capacity to each application by allocating Containers.
A Container is the basic unit of processing capacity in YARN, and is an encapsulation of resource elements

1. CPU
2. Memory
3. Access Mostly Uused Products by 50000+ Subscribers
4. Each Data Node of Hadoop Cluster